Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects about 1 billion people worldwide. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most prevalent type of sleep apnea, which is characterized by recurrent pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses in breathing typically last 10-20 seconds and can occur up to 100 times an hour. During a sleep apnea episode, the lack of oxygen wakes you up, though you may not even recall it. This sleep-disordered breathing causes you to spend more time in light sleep than in deep sleep, leading to inadequate rest.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) is another form of sleep apnea that is caused by the brain not sending signals to the muscles that control breathing. Treating sleep apnea may include Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, lifestyle changes, or surgery. A Sleep Specialist can diagnose and recommend the best treatment for sleep apnea Australia, which can range from mild to severe.
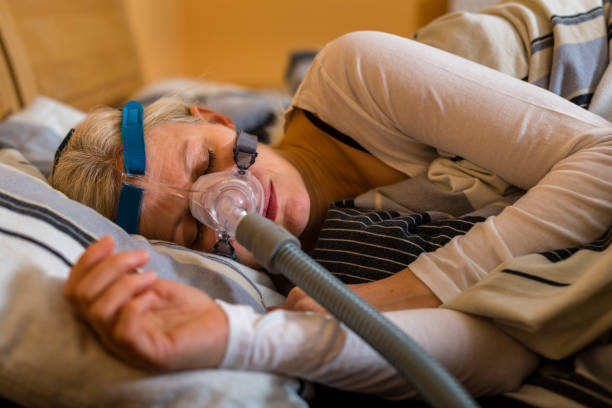
People with severe sleep apnea may be prescribed CPAP to treat the disorder, while people with moderate or mild sleep apnea may benefit from lifestyle changes like weight loss or changes in sleeping positions. A sleep study may be ordered to diagnose sleep apnea and daytime sleepiness.
Treatment of sleep apnea usually involves Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) to deliver air pressure to keep the airways open. Other treatments include lifestyle changes, oral appliances, and surgery. If you are experiencing snoring or gasping while sleeping, it is best to see a sleep specialist to determine if you have sleep apnea and discuss the best treatment plan for you.
So many health conditions can be caused by sleep apnea and in most cases, they could be terminal. Some common ones are-
- Stroke
- Cardiovascular diseases
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
There are primarily two types of sleep apnea, namely-
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Mild sleep apnea
OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea and it occurs when there is a blockage of the upper airways while sleeping. This blockage can cause loud snoring and gasp for air. People with OSA are at risk of developing sleep disorders such as severe, moderate, and mild apnea. To reduce the risk, it is important to avoid anything that could narrow the airways, such as obesity, large tonsils, and changes in hormones.
If you suffer from OSA, it is important to consult a sleep specialist and get a sleep study done to diagnose and treat the issue. Treatments for OSA can involve Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices and other lifestyle changes to help with daytime sleepiness.
CENTRAL SLEEP APNEA
Mild Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a less common and more complex sleep disorder than the first type. It occurs when the brain temporarily stops sending signals to the muscles that control breathing, which can cause you to stop breathing or fall asleep suddenly. OSA is usually caused by an existing health condition, such as those that affects the brain’s control over chest muscles and airways. Most people with Obstructive Sleep Apnea will not experience loud snoring or have any other obvious symptoms. However, if left untreated, OSA can lead to more serious health issues such as high blood pressure and sleep-disordered breathing.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder that affects many people and can be identified by a visit to a sleep specialist or a sleep study. OSA is associated with severe daytime sleepiness and can increase the risk of developing other serious health issues if left undiagnosed or untreated. Symptoms of OSA can range from mild to severe, with severe and moderate forms being the most common.
To diagnose OSA, a physician may recommend a sleep study and the use of Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy to measure the air pressure in your throat. Treatment for OSA can include lifestyle changes such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and smoking, as well as more emergent treatments such as CPAP therapy. People with sleep apnea should be aware of the risk factors associated with the disorder and seek medical attention if necessary.
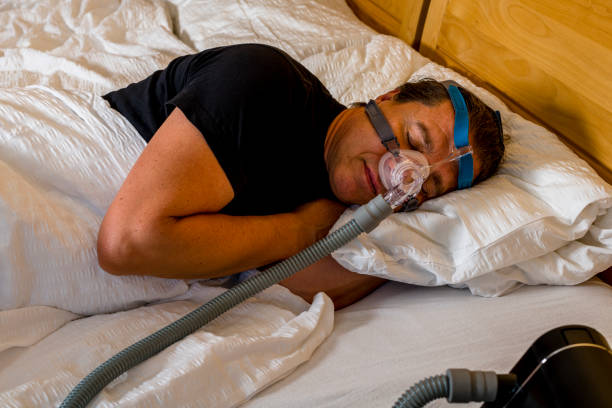

A lot of people around the world live with sleep apnea and are unaware of it due to its prominent symptoms occurring while asleep. Your partner should be able to notice it and inform you of the symptoms, including snoring loudly, restless sleep, trouble concentrating, and pauses in breathing and oxygen levels. If left untreated, people with sleep apnea are at a higher risk of developing other sleep disorders, metabolic syndrome, atrial fibrillation, and emergent central sleep apnea.
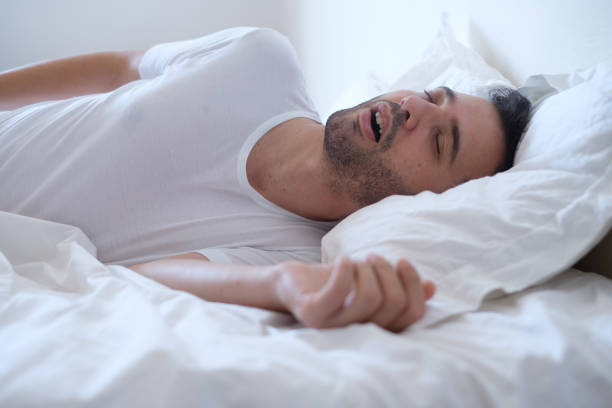

Treatments for sleep apnea include weight loss, oral appliance therapy, other airway pressure devices, and exercises to strengthen the upper airway muscles and soft palate to open the narrowed airway. These treatments can help reduce symptoms and restore normal sleep, breathing, and oxygen levels.
Strong warning signs of sleep apnea are pauses when snoring and choking or gasping sounds.
The main symptoms of sleep apnea include-
- Gasping, snorting, or snoring during sleep
- Frequent, loud snoring
- Drowsiness or sleepiness during the day and fatigue even after sleeping for hours
Other symptoms are-
- Frequently visiting the bathroom at night
- Waking up with a dry mouth and sore throat
- Insomnia or a restless sleep
- Jerking awake at night feeling short of breath
- Headache in the morning
The above symptoms are experienced by people with both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
COULD IT BE JUST LOUD SNORING OR SLEEP APNEA?
People with sleep apnea, a condition in which breathing stops and starts during sleep, can experience loud snoring, fatigue, tiredness, or sleepiness during the day. To be sure if you are suffering from sleep apnea, it is important to visit a sleep specialist. A sleep study can help determine the type and severity of your sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common form of sleep apnea and is characterized by loud snoring and pauses in breathing. A milder form of OSA is called moderate obstructive sleep apnea. Severe sleep apnea is also a form of OSA and it is associated with a higher risk of health problems. Treatments for sleep apnea may include oral appliances, clinical sleep medicine, bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP), sleeping pills, and avoiding upper airway obstruction. It is important to work with your doctor to determine the best treatment option for you.
WHAT SLEEP APNEA CAN DO TO YOUR BODY
Sleep apnea has the ability to worsen underlying illnesses and cause death. It is a condition you should never take for granted. Below is what sleep apnea does to different organs or systems in the body.
Digestive system
People with sleep apnea have higher chances of suffering from fatty liver disease, higher levels of liver enzymes, and liver scarring. It disrupts and disturbs the liver.
This disease could also worsen heartburn and drastically reduce your sleep time.
Respiratory system
Sleep apnea can cause a variety of health complications, such as COPD, asthma, metabolic syndrome, and atrial fibrillation. It is often associated with narrowed airways, loud snoring, restless sleep, and trouble concentrating. An oral appliance, other airway pressure devices, or strengthening of upper airway muscles can help relax the soft palate and open the airway, restoring normal sleep and breathing and oxygen levels. Weight loss can also help reduce the risk of developing sleep apnea and other sleep disorders, such as emergent central sleep apnea.
Cardiovascular systems
Sleep apnea is strongly linked to high blood pressure and obesity and these diseases have a way of putting a strain on your heart. Sleep apnea affects normal heart rhythm and increases your chances of suffering a stroke. Recently, a lot of people with sleep apnea have experienced heart failure.
Reproductive system
If you suffer from sleep apnea, your desire to have sex may be reduced. This especially affects men and could cause erectile dysfunction, affecting their ability to have children.
FACTORS THAT INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF DEVELOPING SLEEP APNEA
Old age- While sleep apnea can occur at any age, your risk of developing it increases as you age. According to research, sleep apnea becomes more prevalent when you hit your 50s or 60s.
Smoking- Smoking has always been known to worsen any condition and even cause it. Studies show that smokers are 3 times more likely to develop sleep apnea than non-smokers.
Weight- If you are overweight, you need to take caution because it is one of the risk factors for sleep apnea. It’s higher for those that are obese
Anatomical differences- Most people don’t know this but there are some physical attributes that could contribute to sleep apnea. Having a deviated spectrum, a small upper airway, enlarged tonsils, and a high tongue position can increase your risk of developing sleep apnea.
FINAL THOUGHTS
If you or your partner begin to notice signs of sleep apnea, such as snoring loudly, restless sleep, trouble concentrating, or other sleep disorders, it is important to visit a doctor for immediate treatment. Sleep apnea can cause chronic sleeping deprivation which leads to an increased risk of developing serious illnesses like metabolic syndrome, atrial fibrillation, and emergent central sleep apnea. To treat sleep apnea, doctors may recommend weight loss, an oral appliance, airway pressure devices, or other airway pressure devices, which help to keep the airway open by strengthening the upper airway muscles or soft palate. These treatments help to improve breathing and oxygen levels, as well as allow for normal sleep
